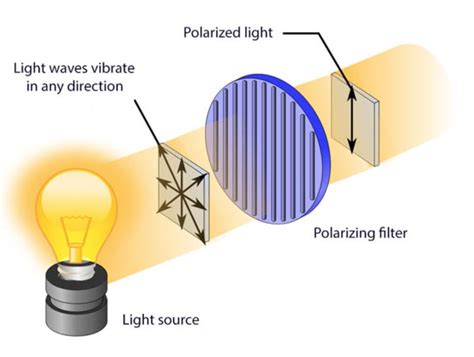
imaging polarimeters|application of polarized light : solution Here we demonstrate a new principle and design for DoFP-PCs based on dielectric metasurfaces with the ability to control polarization and . The festival offers an extraordinary range of artistic events. She must have been an extraordinary artist to work with. I found an extraordinary number of errors in the document. He did the work with extraordinary energy and good humour. He used the extraordinary powers granted to him by Parliament to introduce economic reforms.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Chatrandom aplicativo de bate-papo em vídeo. Sem registro, sem e-mail, sem cartão de crédito. Veja sites como o Chatrandom em TopChatSites.com.
Polarimetric microscopy experiments demonstrate that metalens polarimeters can realize high-resolution polarization imaging for various microscopic samples. This study offers a promising solution for high-resolution .We discuss the foundations of passive imaging polarimetry, the phenomenological reasons for designing a polarimetric sensor, and the primary architectures that have been exploited for developing imaging polarimeters. Polarimetric microscopy experiments demonstrate that metalens polarimeters can realize high-resolution polarization imaging for various microscopic samples. This study offers . Here we demonstrate a new principle and design for DoFP-PCs based on dielectric metasurfaces with the ability to control polarization and .
In this paper we develop several performance prediction tools that can be used to address these needs; these models are based on the micro-polarizer array (MPA) .Imaging polarimeters are often designed and optimized by assuming that the polarization properties of the optics are nearly ideal. For example, we often assume that the linear . Deep learning, as utilized by Lin et al. in Contribution 11, augments the capabilities of polarimetric imaging, achieving high-performance imaging reconstructions. Polarimetric technology can also advance 3D . Advanced research has been adopted in super-resolution imaging harnessing fluorescent dipoles via polarised illumination, with applications such as revealing .
A linear division-of-focal-plane camera combined with a controllable polarization modulator constitutes a versatile full-Stokes imager with four possible sampling rate modes, depending on the number of acquisitions. Considering several . Imaging polarimetry is an emerging sensor technology that promises to improve the performance of sensor systems when used as an adjunct to conventional intensity-based imaging. Several prototype systems capable of being deployed from aircraft are under development. One system has successfully completed an airborne military utility assessment .Imaging polarimeters are often designed and optimized by assuming that the polarization properties of the optics are nearly ideal. For example, we often assume that the linear polarizers have infinite extinction ratios. It is also usually assumed that the retarding elements have retardances that do not vary either spatially or with the angle of incidence. We consider the . Recent developments for long-wave infrared (LWIR) imaging polarimeters include incorporating a microgrid polarizer array onto the focal plane array. Inherent advantages over other classes of polarimeters include rugged packaging, inherent alignment of the optomechanical system, and temporal synchronization that facilitates instantaneous .
polarized light imaging
Stokes imaging spectropolarimeters are versatile instruments to acquire Stokes-vector spectral signatures in a variety of scenes 1,2,3,4,5,6,7.It combines the abilities of an imaging spectrometer .
particular type of imaging instrument. 2. Measurement Considerations The basic aspects of light that are typically measured in imaging scenarios are intensity, spectral content, coherence, and polarization. For passive imaging po-larimetry, it is often most convenient to represent the polarization information in terms of the Stokes vector, Two configurations of imaging polarimeters are described that are designed for polaimetric optical metrology. The first is a Stokes imaging polarimeter which measures the polarization response of optical systems to spherical or planar waves of known polarization. The output is images of the degree of polarization, orientation, and eccentricity of polarization .
The design, components and calibration of a 4 camera polarimetric system that operates in the visible to near IR spectrum and is capable of a 25Hz Stokes image frame rate is summarized. Recent interest in the utility of polarimetry for military and commercial applications has led to the development of many different imaging polarimetric systems. Much of the . The design and construction of wide FOV imaging polarimeters for use in atmospheric remote sensing requires significant attention to the prevention of artificial polarization induced by the . Imaging polarimeters typically utilize polarizing arrays located in front of a focal plane array as a means of extracting polarization information from the optical scene. Over the last few years . Model for imaging polarimetry. In the imaging polarimetry model, a WGP is placed at the focal length (f) of an imaging convex lens (f-number f/#).For the convenience of analysis, we have assumed .
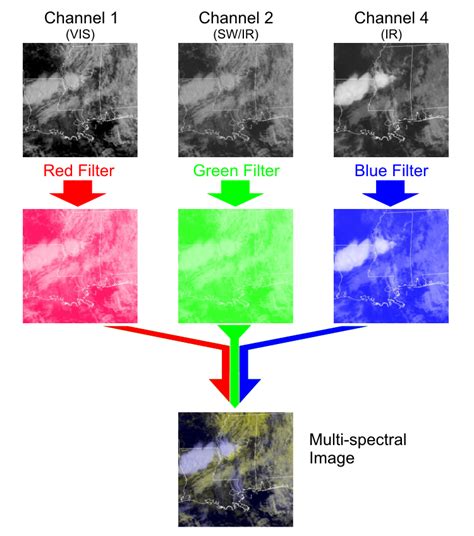
polarization multispectral imaging
Long-wave infrared imaging Stokes vector polarimeters are used in many remote sensing applications. Imaging polarimeters require that several measurements be made under optically different conditions in order to estimate the polarization signature at a given scene point.
Imaging polarimetry is an emerging sensor technology that promises to improve the performance of sensor systems when used as an adjunct to conventional intensity-based imaging. Several prototype systems capable of being deployed from aircraft are under development. One system has successfully completed an airborne military utility assessment . Four types of single-snapshot full-Stokes division-of-aperture imaging polarimeter with four subapertures are presented and compared, with maximum spatial resolution for each polarimetric image on a single area-array detector. Single-snapshot full-Stokes imaging polarimetry is a powerful tool for the acquisition of the spatial polarization information in real .
polarized test
Polarization is a general descriptor of light and contains information about reflecting objects that traditional intensity-based sensors ignore. Difficult computer vision tasks such as image segmentation and object orientation are made tractable with polarization vision techniques. Specularities, occluding contours, and material properties can be readily extracted if the .Retrieval of Mueller matrices from intensity measurements is a noise-sensitive process. In addition, the choice of the method used for extracting Mueller matrix elements greatly influences the precision of the final results. Among available procedures, three have been tested and their robustness analyzed by adding Gaussian noise to computer synthesized data and have been .
Single-snapshot full-Stokes imaging polarimetry is a powerful tool for the acquisition of the spatial polarization information in real time. According to the general linear model of a polarimeter, to recover full Stokes parameters at least four polarimetric intensities should be measured. . the performance of four polarimeters are evaluated . Polarization, a core attribute of light waves, offers insights into light’s physical properties and its interactions with materials [1,2].This unique aspect of polarization paves the way for its application across a broad range of fields, from object detection and biomedical imaging to remote sensing and beyond [3,4,5,6].This Editorial is part of the Special Issue . For almost 20 years, microgrid polarimetric imaging systems have been built using a 2×2 repeating pattern of polarization analyzers. In this Letter, we show that superior spatial resolution is achieved over this 2×2 case when the analyzers are arranged in a 2×4 repeating pattern. This unconventional .
For almost 20 years, microgrid polarimetric imaging systems have been built using a 2×2 repeating pattern of polarization analyzers. In this Letter, we show that superior spatial resolution is achieved over this 2×2 case when the analyzers are arranged in a 2×4 repeating pattern. This unconventional result, in which a more distributed sampling pattern results in . Modern dual-beam polarimeters (imaging and non-imaging) routinely operate with sensitivities a factor of 10–100 lower than RITPIC. Micropolarizer-based polarimeters are not suitable for applications that require sensitivity greater than ∼0.1%. On the other hand, this still leaves many science cases that can be studied with these detectors . In addition, imaging polarimeters have the potential to be efficient detectors owing to their superiority in terms of their capability of recognizing object contours and surface roughness. In this paper, the polarization changes of stone materials with different angles and varying degrees of roughness are theoretically analyzed and detected by .
polarization images
Imaging polarimeters are often designed and optimized by assuming that the polarization properties of the optics are nearly ideal. For example, we often assume that the linear polarizers have infinite extinction ratios. It is also usually assumed that the retarding elements have retardances that do .Significance: Reflection Mueller matrix imaging is suitable for characterizing the microstructure of bulk specimens and probing dynamic processes in living animals, there are always demands for speed and accuracy for such applications to avoid possible artifacts and reveal a sample's intrinsic properties. Aim: To demonstrate a design of collinear reflection Mueller matrix fast .
Imaging polarimetry has the potential to be a key sensor technology in a number of target detection applications. Imaging polarimeters measure the polarization state of light emitted from and/or reflected from scenes. The light is polarized because of the geometry, roughness and material properties of the objects embedded in the scene. This added .Two configurations of imaging polarimeters are described that are designed for polaimetric optical metrology. The first is a Stokes imaging polarimeter which measures the polarization response of optical systems to spherical or planar waves of known polarization. The output is images of the degree of polarization, orientation, and eccentricity of polarization ellipses, or . 1. Introduction. Imaging polarimeters have attracted increasingly attention in many regions due to their excellent detection and identification abilities [[1], [2], [3]].In general, a imaging polarimeter is composed of the front optical system (FOS), polarization measurement module and imaging component and FOS are commonly those optics in front of polarization .
polar coordinates in biomedical imaging
full stokes polarization images
full stokes polarization camera
web10 cuidados para comprar na Shopee de forma segura. 1. Atente-se aos detalhes do produto (peso, tamanho e quantidade) A primeira coisa que você deve fazer ao se interessar por um produto é prestar atenção nos detalhes do produto. Veja qual o peso, quantidade e tamanho do produto a ser comprado, para saber se é isso mesmo que você deseja.
imaging polarimeters|application of polarized light